What Function Do the Wind-driven Currents Play in the Transport
As these currents flow westward the Coriolis effecta force that results from the rotation of the Earthdeflects them. For example upwelling takes place along much of the equator.

Wind Driven Circulation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The Southern Ocean contains a large wind-driven current the Antarctic Circumpolar Current which carries approximately 170 10 6 m 3 of water eastward around Antarctica within multiple filamented jets.

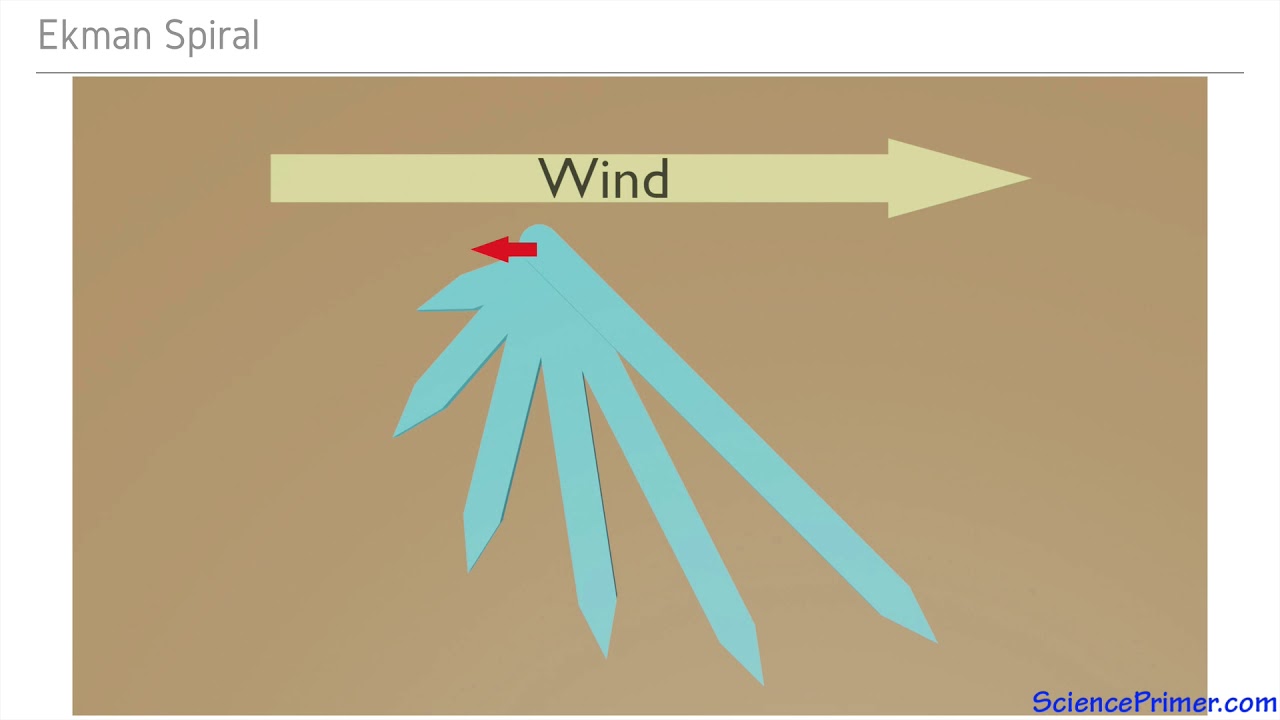
. 1 wind-driven circulation forced by wind stress on the sea surface inducing a momentum exchange and 2 thermohaline circulation driven by the variations in water density imposed at the sea surface by exchange of ocean heat and water with the atmosphere inducing a buoyancy exchange. Surface currents are driven by. -when driven by wind topmost layer of water in N hemisphere flows at about 45 degrees to right of wind direction Coriolis -water in next layer cannot feel the wind at surface it feels only the movement of the water immediately above.
These currents transfer heat from the tropics to the Polar Regions influencing local and global climate. Wind-driven currents Bring nutrients from deep water up into shallow water Also it influences weather patterns. In the example of the gulf stream this transfer of heat to the air warms up England and Europe.
Wind driven currents like the gulf stream for example originate in the equatorial and warm areas of the earths oceans. Large-scale surface ocean currents are driven by global wind systems that are fueled by energy from the sun. What function do the wind-driven currents play in the transport of heat energy in the oceans.
Water equatorward transport 10-15 Sv Trade wind-driven current the moderately shallow and broad westward current transport 30 Sv Westerly-driven current the wider and slower than the trade wind-driven current eastward current Figure from Oceanography by Tom Garrison Volume transport unit. As the water cools its density upsurges because of chilling and. A steady wind stress causes a transport of the surface water 90 to the right of the wind direction in the Northern Hemisphere and 90 to the left in the Southern Hemisphere because of the combined action of the wind stress on the ocean surface and the Coriolis force.
As a result the surface currents and the deep currents are linked. Wind-driven currents are maintained by momentum transferred by the winds to the ocean surface. The winds pull surface water with them creating currents.
Deep clear pan or tub. Wind causes surface currents to transport water around the oceans while density differences cause deep currents to re. What function do the wind-driven currents play in the transport of heat energy in the oceans.
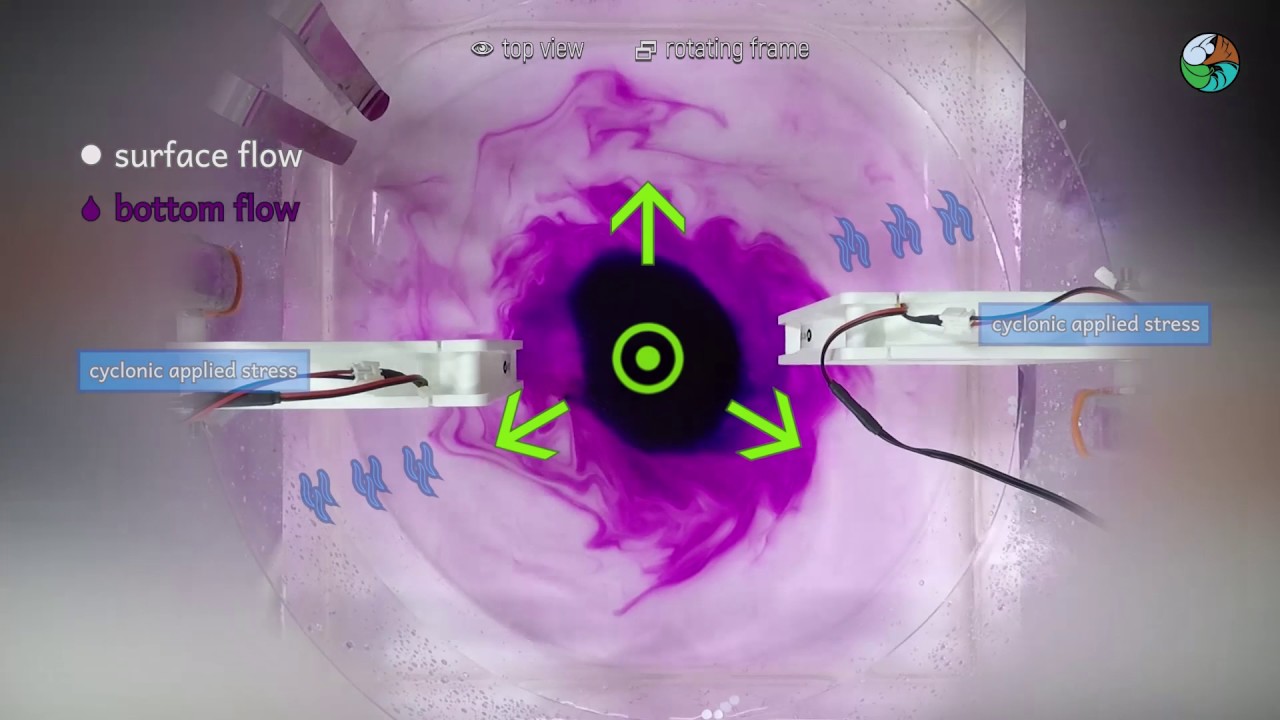
Upwelling and downwelling also occur in the open ocean where winds cause surface waters to diverge move away from a region causing upwelling or to converge toward some region causing downwelling. The net wind-driven movement of water known as Ekman transport creates a bulge in each ocean basin that is as much as three feet one meter higher than mean global sea level. As a result the surface currents and the deep currents are linked.
The currents then bend to the right heading north. The currents then transmit the warm water north where the heat in the water is misplaced to the colder atmosphere. The currents then carry the warm water north where the heat in the water is lost to the colder atmosphere.
Ocean currentsdefine two circulation types. Isotropic and anisotropic responses near the coast can be applicable to wind -driven surface transport model in the coastal regions. The ocean is not a still body of water.
What Function Do The Wind-driven Currents Play In The TransportCooler water is more dense so it begins to sink. Cooler water is more dense so it begins to sink. In the instance of the Gulf Stream this transmission of heat to the air warms up England and Europe.
Earths rotation results in the Coriolis Effect which also influences ocean currents. Haline salinity in the deep ocean and wind-driven currents on the surface. It transports heat from the Tropics to cooler areas.
What Function Do The Wind-driven Currents Play In The Transport. -deeper layer of water moves at angle to right by overlying water. Ocean the wind sets the surface waters in motion as a current the Coriolis force the density distribution of sea water and the shape of the ocean basin.
Surface currents are driven by wind and the rotation of the Earth. As wind blows over the ocean surface an Ekman current develops due to the drag at the wind-water interface and it deflected to the right due to the. What function do the wind-driven currents play in the transport of heat energy in the oceans.
To the south of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current within the Antarctic marginal seas the Weddell Gyre transports water cyclonically clockwise. Ekman current is the surface current caused by steady wind at the surface wind-driven surface-current. Wind causes surface currents to transport water around the oceans while density differences cause deep currents to return that water back around the globe Figure 1417.
The great ocean conveyor moves water around the globe. Wind driven currents create in the equatorial and warm zones of the earths oceans. The grey shapes on the left are clouds.
1 sv 1 Sverdrup 1 million m3sec. The force of gravity pulling on this large mass of water creates a pressure gradient similar to that in an atmospheric high pressure system which in turn leads to a. There is constant motion in the ocean in the form of a global ocean conveyor belt.
Environmental parameterization using wind -current transfer function provides statistical framework consistent with analytic solutions derived from linearized momentum equations. This motion is caused by a combination of thermohaline currents thermo temperature.
What Function Do The Wind Driven Currents Play In The Transport Lisbdnet Com

Wind Driven Circulation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

What Function Do The Wind Driven Currents Play In The Transport Lisbdnet Com
Comments
Post a Comment